
How to Print
“How To Print” is the project I completed during the course of my Pitch Your Own Design Internship this summer at Poster House. It is a series of educational illustrations and graphics on printmaking compiled into a booklet that unfolds into a poster. It is not a comprehensive guide, but rather an approachable overview on three types of printmaking used to produce posters: stone lithography, screen printing, and Risograph printing. The goal of this project was to make an accessible and visually engaging tool that can be used to teach anyone about printmaking. We developed ”How to Print” with elementary to high school-aged students in mind, since it will be used by and distributed during Poster House’s school partnerships.











In true Poster House fashion, the reader can unfold the booklet into a poster!
What is printmaking?
Printmaking involves the transfer of an image from a matrix, or template, to a substrate using ink and pressure. Multiple copies can be printed from the same matrix, allowing designers to quickly create large batches of prints. A common method to produce multi-color images is to use different matrices to print layers on top of each other, each using a different color ink.
Stone Lithography
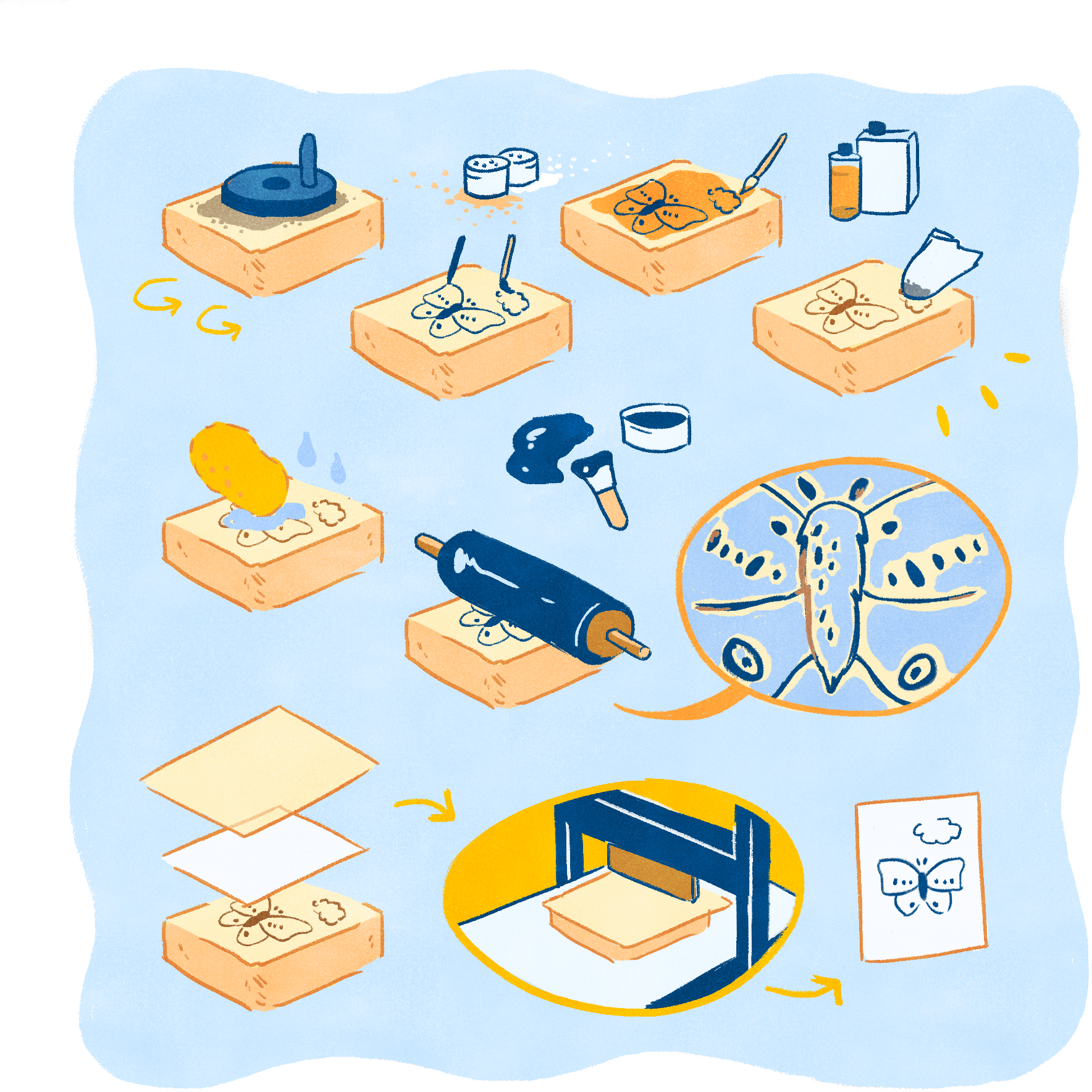
Stone Lithography Illustration
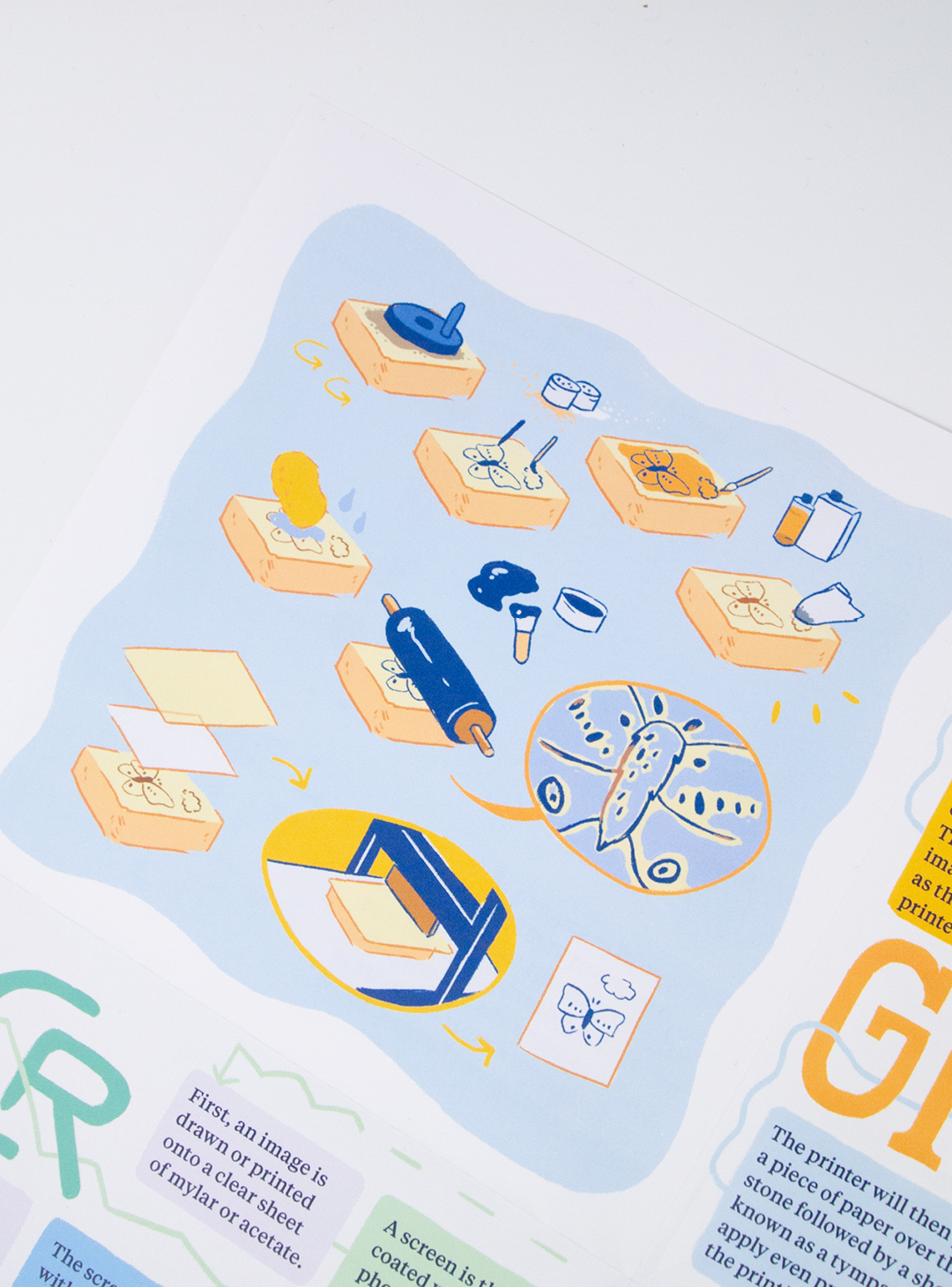
Stone lithography is a printing method involving oil and water resistance on a flat limestone block.
- First, the stone’s surface is grained smooth by rubbing it with another stone or a tool called a levigator, along with coarse grit and water.
- A designer then draws on the stone with a grease or wax based medium. The drawing is the mirror image of the final design, as the image will be printed in reverse.
- Chemicals such as rosin, talc, gum arabic, and lithotine are then applied to the entire surface to lock the image into the stone. The blank areas will now absorb water, while the areas with the design will absorb ink.
- After wiping away the original image, the stone is then wet with a damp sponge and inked with a roller. The ink sticks to the areas occupied by the drawing, but is rejected by the areas wet with water. This process is repeated until the image is fully inked.
- The printer will then place a piece of paper over the stone followed by a sheet known as a tympan that will apply even pressure during the printing process.
- The stone is then put through a printing press, which applies pressure and pushes the inked image onto the paper.
Screen Printing

Screen Printing Illustration
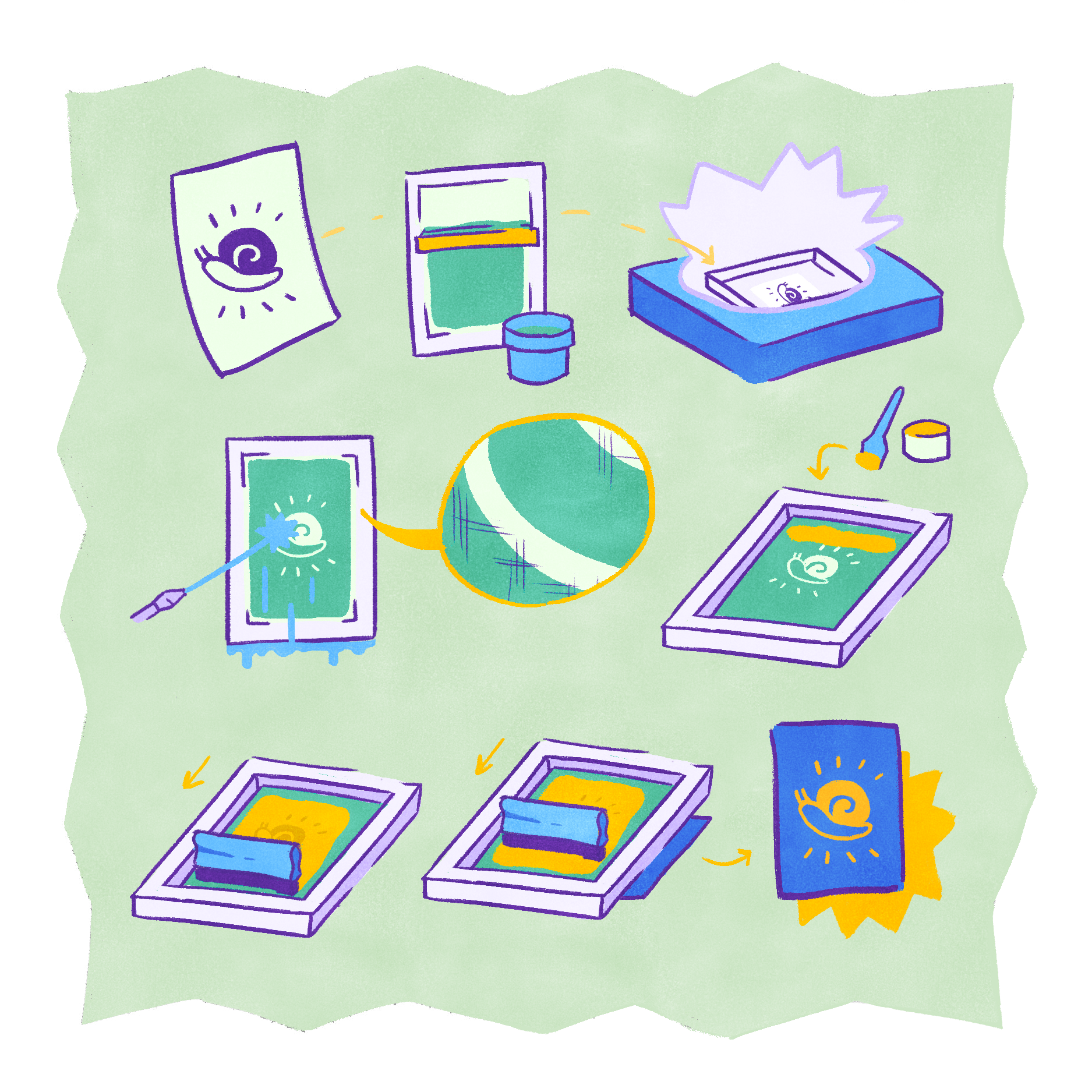
Screen printing is the process of pushing ink through a stenciled mesh screen to create a design.
- First, an image is drawn or printed onto a clear sheet of mylar or acetate.
- A screen is then coated with a photosensitive emulsion over which the design is attached.
- This combination is placed inside an exposure unit that projects UV light through the piece, fixing the stenciled image to the emulsion coating.
- The screen is rinsed with water, exposing the areas previously blocked by the image and creating a stencil within the mesh.
- The printmaker then pours ink onto the top of the screen and uses a squeegee to drag it across the surface. This process—called flooding—presses ink through the open parts of the stencil where the emulsion was washed off.
- A substrate is placed beneath the screen and the squeegee is dragged down again, pushing more ink through the stencil and printing the image.
- This process can be repeated depending on how many additional colors the designer wishes to include in the print.
Risograph Printing
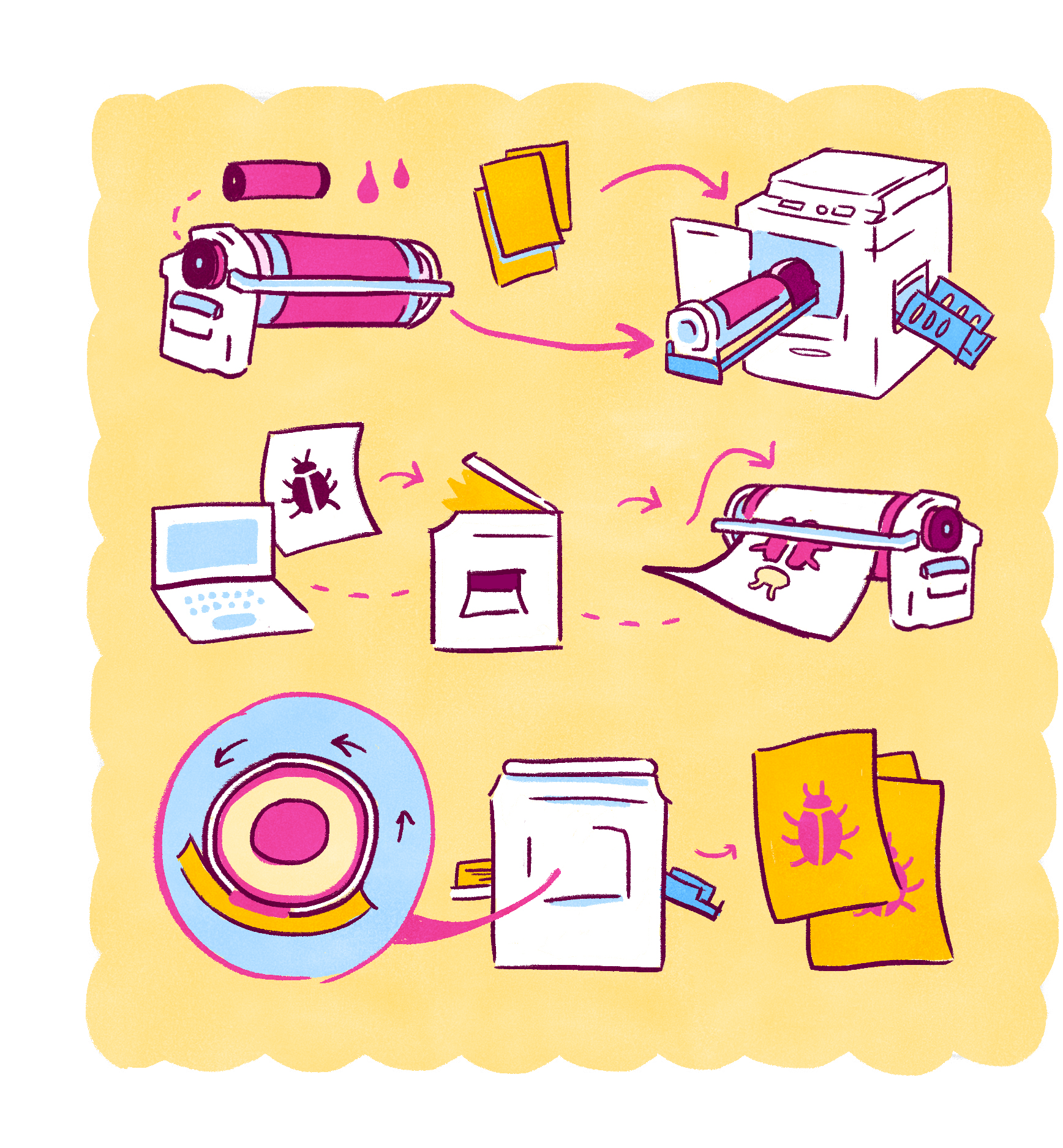
Risograph Printing Illustration
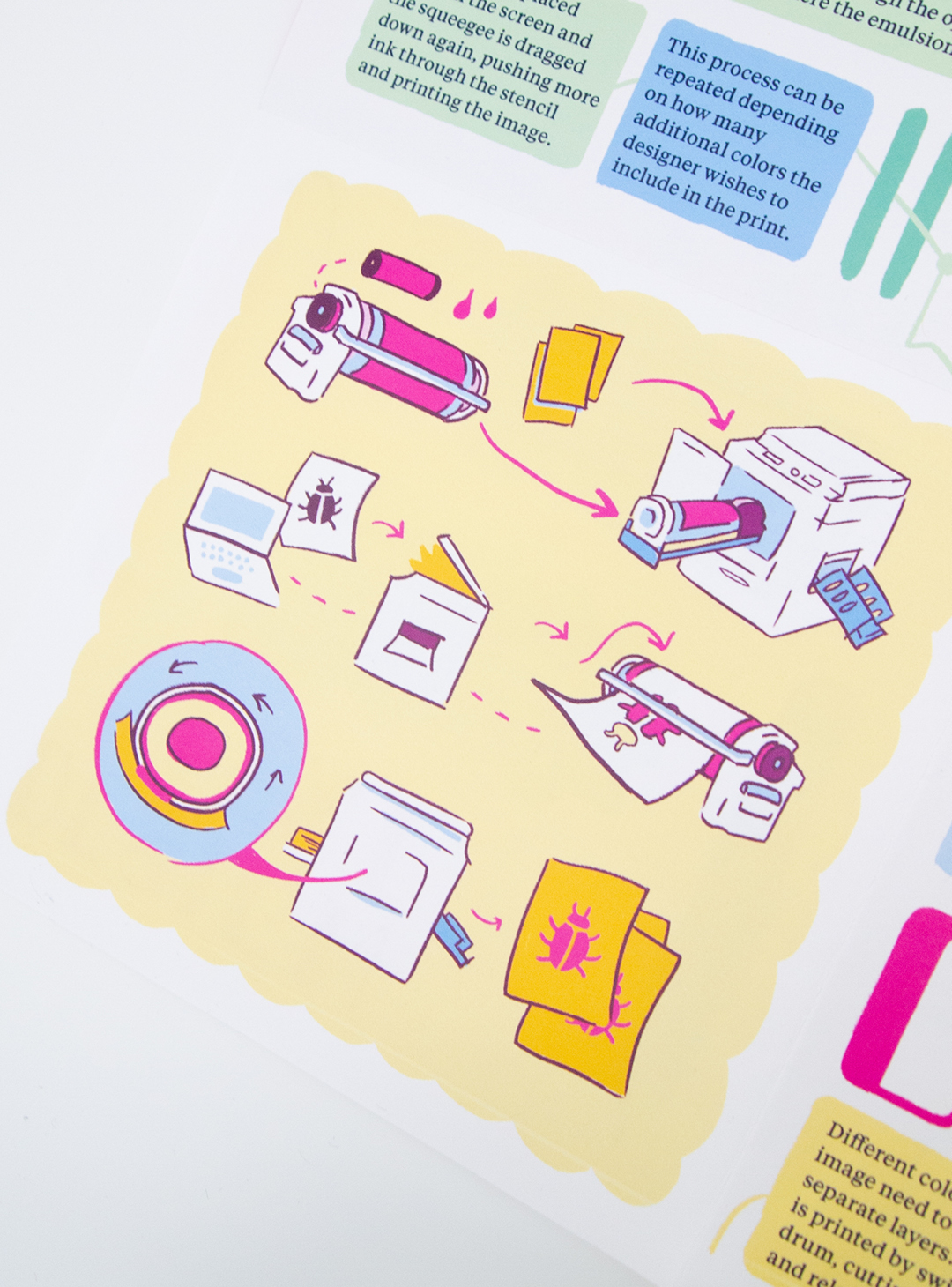
Risograph printing is a stencil-based printing method executed by a digital duplicator machine called a Risograph.
- The designer first loads paper and a drum containing one color of ink into the printer.
- The initial layer is digitally uploaded to the Risograph either through a file or scanner. This information is used to create a stencil on rice paper.
- The Risograph wraps the ink drum with the stencil, blocking out the negative areas of the design.
- When printing is initiated, ink is pushed out of the spinning drum, through the stencil, and onto each piece of paper.
- Different colors in an image need to be printed as separate layers. A new color is printed by switching the drum, cutting a new stencil, and reloading the paper.
Design and Text
This booklet was developed and designed by Erin Moore as a part of her Pitch Your Own Design Internship with Poster House in Summer 2021. Guidance was provided by mentors Ola Baldych and Mihoshi Fukushima Clark, and content editing was done by Angelina Lippert.
Internships
Poster House is pleased to offer paid internship opportunities for undergraduate students, graduate students, and recent grads in various museum departments. For more info please contact internships@posterhouse.org.
